


Next:9.10
Merge SortUp:9.
Sorting MethodsPrevious:9.8.2
Result 2: Lower Bound on Average Case Complexity
9.9 Radix Sorting
Example
-
n = 10
-
Initial list : 36, 9, 0, 25, 1, 49, 64, 16, 81, 4
Phase 1 : bin = i mod 10
= right most digit of i
| Bin |
|
|
| |
|
|
| 0 |
| 0 |
 |
|
|
| |
|
|
| 1 |
|
| 81 |
 |
|
| 2 |
|
|
| 3 |
|
|
| 4 |
|
| 4 |
 |
|
| |
|
|
| 5 |
|
|
| |
|
|
| 6 |
|
| 16 |
 |
|
| |
|
|
| 7 |
|
|
| 8 |
|
|
| 9 |
|
| 49 |
 |
|
-
Concatenation would now yield the list:
L: 0, 1, 81, 64, 4, 25, 36, 16, 9, 49
Phase 2 : bin = 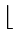 i/10
i/10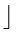
= right most digit of i
-
The concatenation now yields:
0, 1, 4, 9, 25, 36, 49, 64, 81
In general, assume that the key-type consists of k components f1,
f2, ... , fk, of type t1,
t2, ... , tk.
Suppose it is required to sort the records in lexicographic order of
their keys. That is,
(a1, a2,..., ak)
< (b1, b2,..., bk)
if one of the following holds:
| 1. |
a1 < b1 |
| 2. |
a1
= b1;a2 < b2 |
| 3. |
a1
= b1;a2 = b2;a3
< b3 |
| |
. |
| |
. |
| |
. |
| k. |
a1
= b1;...;ak - 1 = bk -
1;ak < bk |
Radix sort proceeds in the following way.
First binsort all records first on fk, the
least significant digit, then concatenate the bins lowest value first.
Then binsort the above concatenated list on fk -
1 and then concatenate the bins lowest value first.
In general, after binsorting on fk,
fk - 1,..., fi, the records will
appear in lexicographic order if the key consisted of only the fieldsfi,...,
fk.
void radixsort;
/ * Sorts a list A of n
records with keys consisting of fields
f1,..., fk
of types t1,...,
tk. The function uses k
arrays B1,...,
Bk of type array [ti] of
list-type, i = 1,...,
k,
where list-type is a linked list of records */
{
for(i = k;i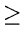 1;i - -)
1;i - -)
{
for (each value v of type ti)
make Bi[v] empty; /*
clear bins */
for (each value r on list A)
move r from A onto the end of bin Bi[v],
where v is the value of the field fi
of the key of r;
for (each value v of type ti
from lowest to highest)
concatenate Bi[v] onto the end of
A
}
}
-
Elements to be sorted are presented in the form of a linked list obviating
the need for copying a record. We just move records from one list to another.
-
For concatenation to be done quickly, we need pointers to the end of lists.
Complexity of Radix Sort



Next:9.10
Merge SortUp:9.
Sorting MethodsPrevious:9.8.2
Result 2: Lower Bound on Average Case Complexity
eEL,CSA_Dept,IISc,Bangalore
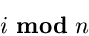 Each
bin will then contain a list of integers leaving the same remainder when
divided by n.
Each
bin will then contain a list of integers leaving the same remainder when
divided by n.