Release 1
Kalyan Ch & Jayanth Gavini.
As per the requirements of the system, we first identified
the actors in the system as Buyer, Seller and Coordinator.
The basic use-cases of the system are: Buy the
product, Sell the product and Co-ordinate trading process.
1.2. DETAILED USE CASE DIAGRAM:
The actors identified in this phase is Trader (who can be a buyer or a seller)
The use cases captured in the detailed use case analysis
are: Register, Login , Logout, Create Agent, Remove Agent, Revise
Product details, Select Business Model, Check Status, Coordinate Trading.
1.3.
DESCRIPTION OF USE CASES:
"REGISTER" USE CASE:
1. The User is provided with the Registration form.
2. The user fills the registration form and submits it (E1)
3. The system checks whether the information is complete and inserts the data in the database (E2)
4. The system sends the confirmation page to the user.
Alternate Flows:
E1:
1. The input parameters are incorrect or the form is not filled properly.
2. The system provides the form again to enter the correct and complete information.
E2:
1. The ID chosen by the user may be in use by some other user .The system provides a page for the user to register with some other ID.
"CREATE AGENT" USE CASE:
Main flows:
1. The system provides the page for creating an agent (buyer or seller).
2. The user fills the details like agent name, product details and all the necessary parameters and submits it (E1).
3. The system provides the confirmation page that the agent is created successfully.
Alternate flows:
E1:
1. The agent details provided by the user are incomplete.
2. The system provides the page again to the user to enter the information completely and correctly.
The classes are identified by examining nouns occurring in various use
cases and actors in the detailed use case diagram.
Types of Classes:
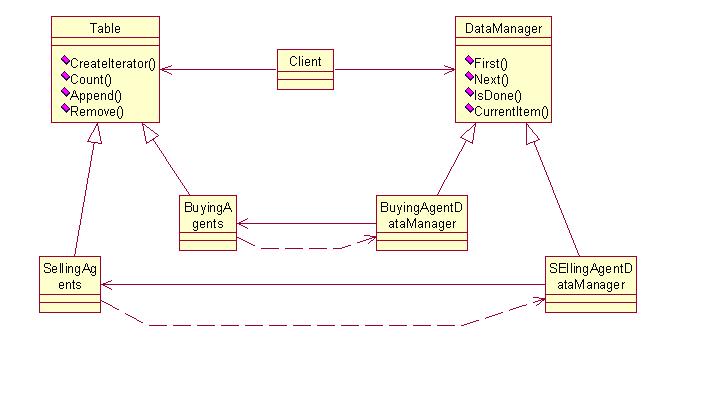
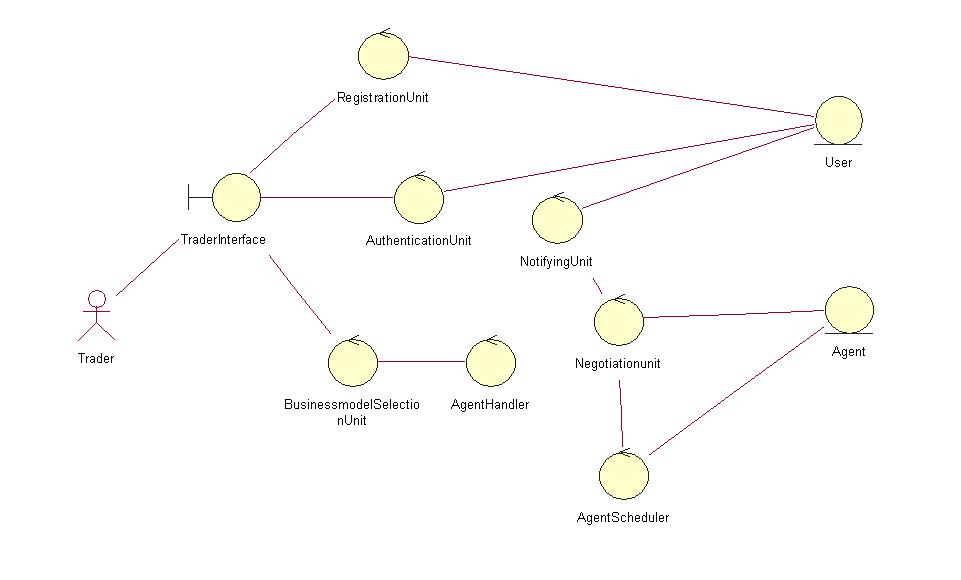
·Boundary class: Boundary class is used to model interaction between the system and its actors. Boundary classes model the parts of the system that depends on its actor. In the above figure, boundary class is Trader interface.
·Control class: Control classes represent coordination, sequencing, transactions, transaction and control of other objects and are often used to encapsulate control related to a sequence use case. In the above figure, control classesare Registration Unit, Authentication Unit, Agent handler, Business Model Invocation Unit.
·Entity class: An entity class is used to model information that is long lived and persistent. Entity classes are derived directly from a corresponding business entity class with in the business object model. In the above figure, entity classes are Buying Agents, Selling Agents and Users.
Sequence diagrams pictorially depict the sequence in which the actions are being performed in every use case. The following are the sequence diagrams for various use cases.
2.2.1.
"REGISTRATION" USE CASE:
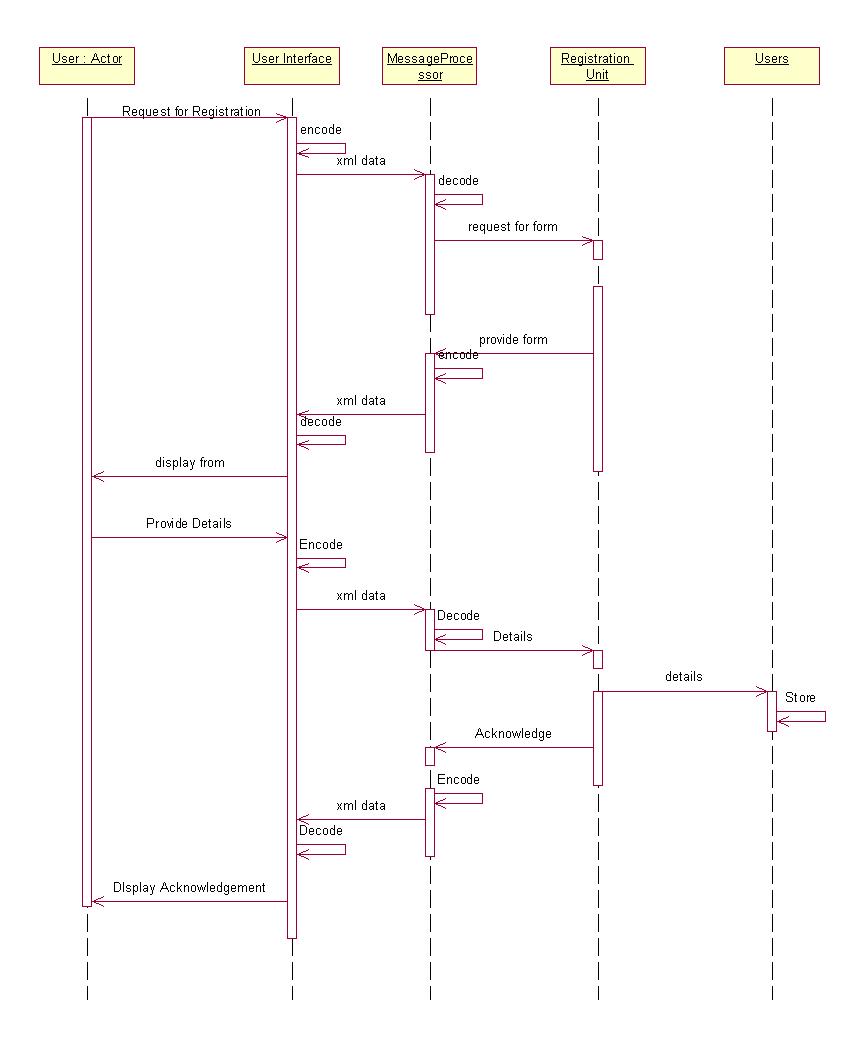
2.2.2.
"CREATE AGENT" USE CASE:
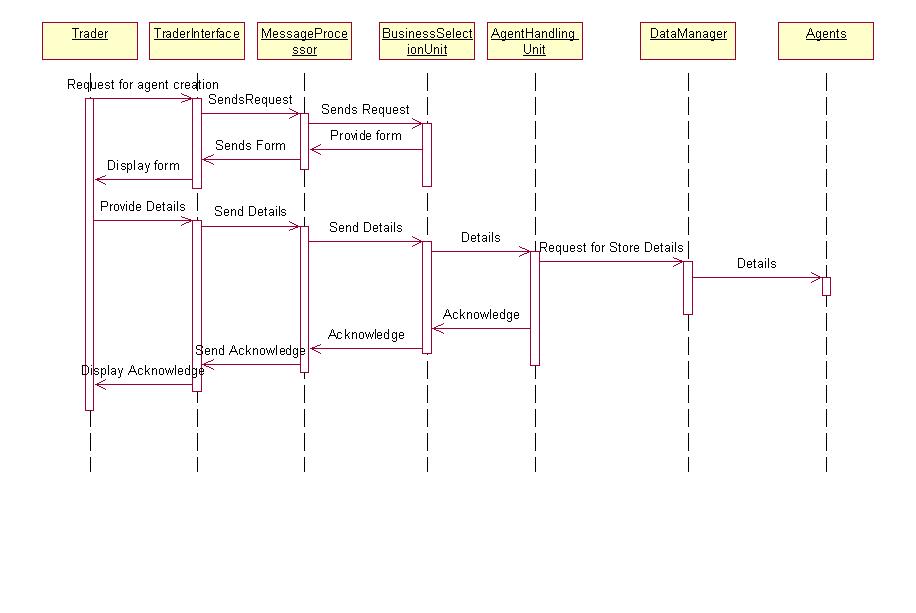
2.2.3. "CO-ORDINATE
TRADING" USE CASE
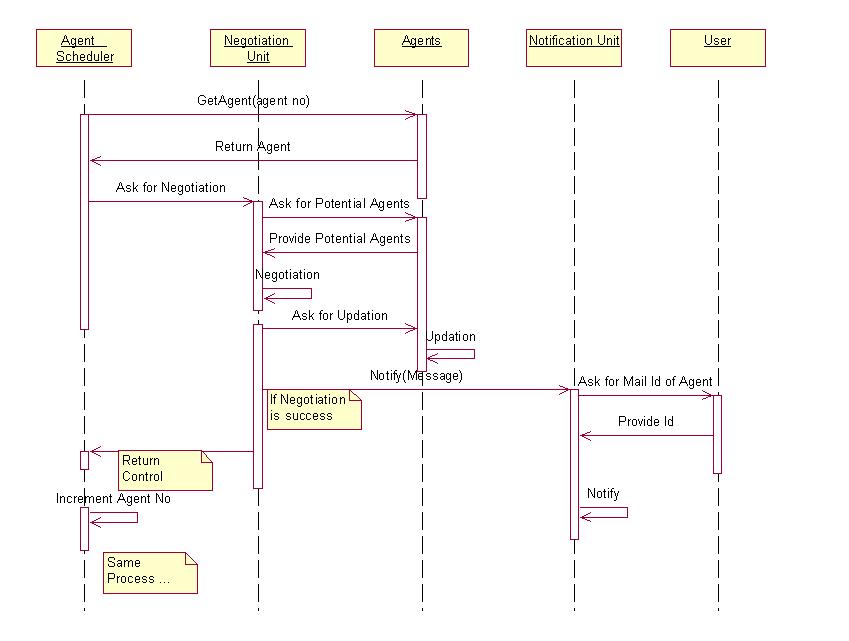
The following is the state chart diagram for the co-ordinate trading in KASBAH :
Thefollowing
is the activity diagram for the KASBAH business model.
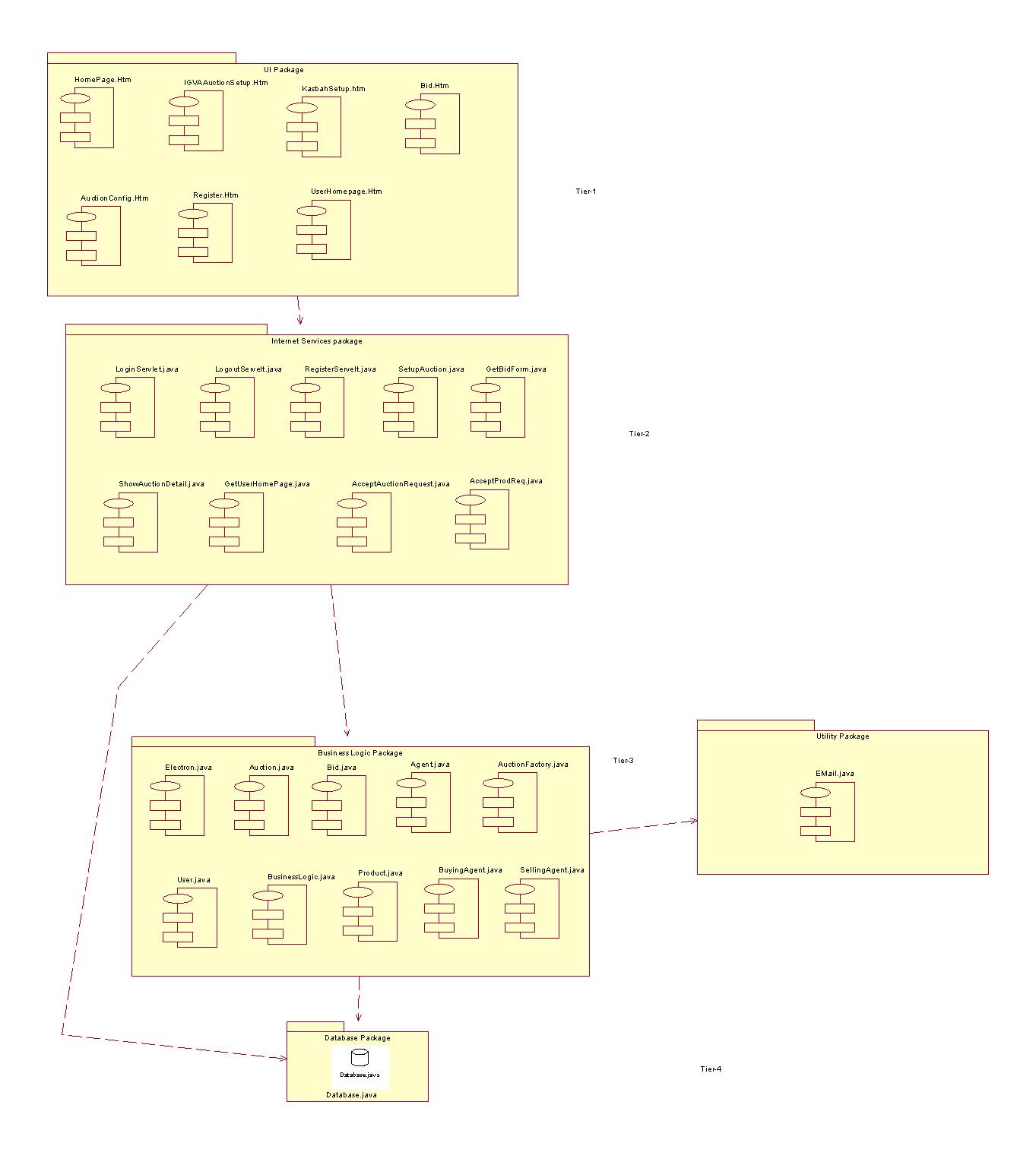
The figure below depicts the preliminary architecture of the system which is obtained by enhancingthe collaboration diagram.
The Architecture of the system is a 3 -Tier Thick Client Architecture.
Tier 1 consists of User Interface.
Tier 2 consists of all the business logic of the system.
Tier 3 consists of database of the system.
NOTE: In Tier 2, we
have a class called Business Model Invocation Unit which invokes the model
currently chosen by the user. We can add any number of Business models
to the system in Tier 2 and just update the Business Model Invocation Unit.

TOP
3.2. DETAILED
CLASS DIAGRAM
3.2.1. DESCRIPTION
OF CLASSES:
Trader Interface:This
class provides an interface to the user so as to communicate with the system.
The interface may be a web page (HTML page).
Message Processor: The class, ?Message Processor?
is present on the client side and the server side. The basic functionality
of this class is to decode the message and construct the message. That
is, encode_message( ) function constructs a message (XML document). Similarly,
decode_message( ) function extracts data from the received message (XML
document) and does the corresponding action. It is the duty of message
processor to invoke the corresponding classes when a message is received.
Registration Unit: This class is invoked when the users wants to register themselves in the site. The basic functionality of this class is that it validates the registration form submitted by the user and inserts his entries in the database.
Authentication Unit: This class is invoked
if the user is already registered and when he wants to enter the site.
The basic functionality of this class is that it authenticates the user
by evaluating the login information submitted by the user.
Data Manager: This class acts as an interface
between Tier 2 and Tier 3. This class performs the tasks like insertion
of data into the database, deletion of data, updation of data and selection
of data from the database. This is the only class which has accessibility
to the database.
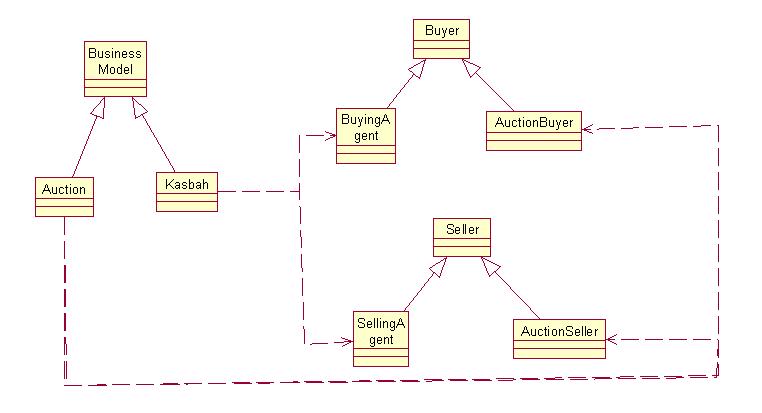
Business Model Invocation Unit: The basic functionality
of this class is to invoke the business model which the user has chosen
(Like Kasbah or Auction etc.)
Payment Unit: The function of this class is
to validate the accounts of the buyer and seller and transfer the amount.
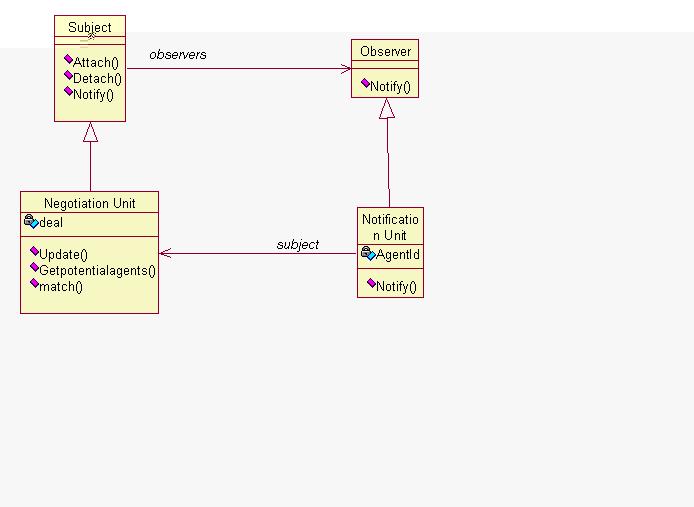
Notification Unit: This unit is used for the
notification of any message to the registered users. The function of this
unit is to e-mail the messages.
Delivery Unit:This
unit takes care of deliver of the product after the validation of accounts.
Agent Scheduler: The function of this is to
give chance to every agent in the market place and passing it to negotiating
unit. It is the duty of the agent scheduler to update the details of the
agents based on the parameters provided by the user as the time progresses
if there is no match found and also that it is its responsibility to notify
the agents when a match is found or when the time is out.
Negotiating Unit: This unit performs negotiation
the agent chosen by the agent scheduler and the potential customers(buyers
or sellers), that is potential buyer if a selling agent is chosen and potential
seller if a buying agent is chosen.
Agent Handler: This unit has the methods like
create_agent(), update_agent() and remove_agent() which correspondingly
creates, updates and removes the agents depending on the user?s choice
.